Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
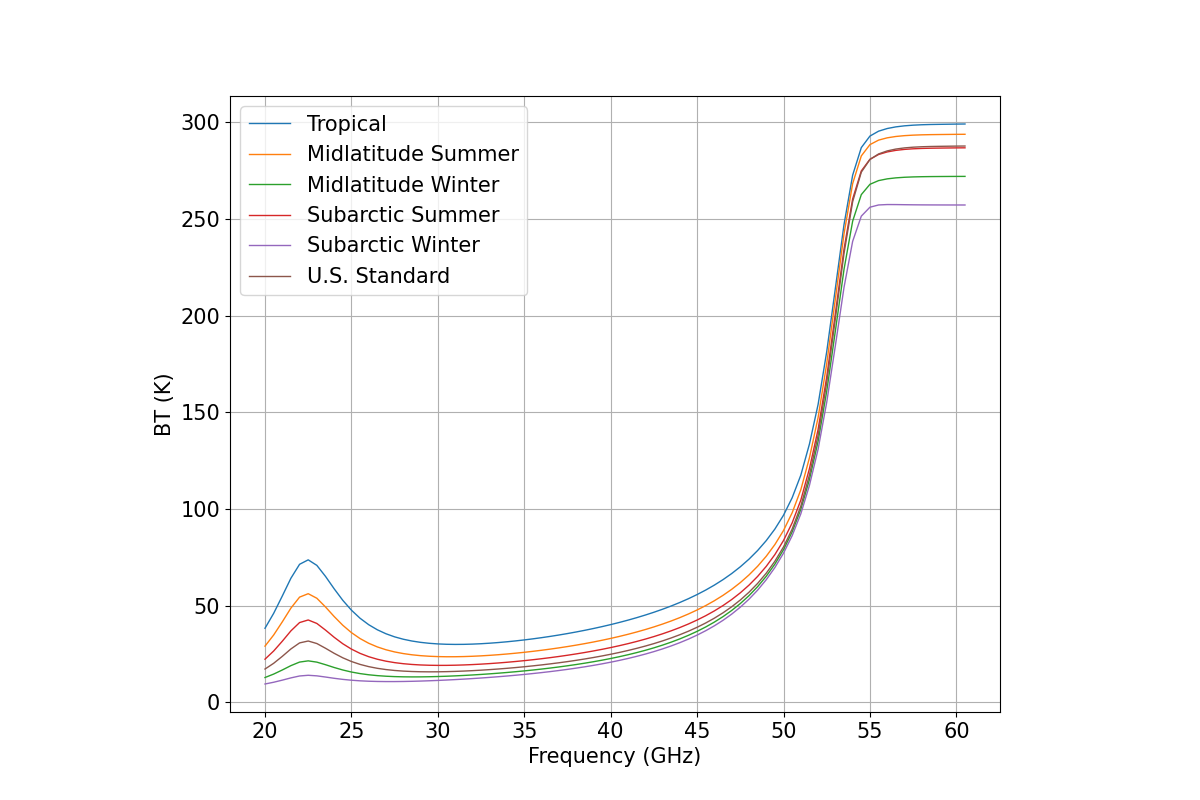
Performing Downwelling Brightness Temperature calculation#
This example shows how to use the
pyrtlib.tb_spectrum.TbCloudRTE method to calculate zenith downwelling brightness temperature
for six reference atmosphere climatology with the R17 model.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 15})
import numpy as np
from pyrtlib.climatology import AtmosphericProfiles as atmp
from pyrtlib.tb_spectrum import TbCloudRTE
from pyrtlib.utils import ppmv2gkg, mr2rh
atm = ['Tropical',
'Midlatitude Summer',
'Midlatitude Winter',
'Subarctic Summer',
'Subarctic Winter',
'U.S. Standard']
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 8))
for i in range(0, 6):
z, p, d, t, md = atmp.gl_atm(i)
gkg = ppmv2gkg(md[:, atmp.H2O], atmp.H2O)
rh = mr2rh(p, t, gkg)[0] / 100
mdl = 'R17'
ang = np.array([90.])
frq = np.arange(20, 61, 0.5)
nf = len(frq)
ax.set_xlabel('Frequency (GHz)')
ax.set_ylabel('BT (K)')
rte = TbCloudRTE(z, p, t, rh, frq, ang)
rte.satellite = False
rte.init_absmdl(mdl)
df = rte.execute()
df = df.set_index(frq)
df.tbtotal.plot(ax=ax, linewidth=1, label='{}'.format(atm[i]))
ax.grid(True, 'both')
ax.legend()
ax.set_box_aspect(0.8)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 12.177 seconds)
